Setting Jdk In Visual Studio Code
- Android Studio Jdk Download
- Android Studio Jdk
- Android Studio Jdk Setting
- Android Studio Jdk Version
- Configure Jdk In Visual Studio Code
This tutorial shows you how to create a Java web application with Visual Studio Code. You'll learn how to run, debug, and edit the Java web app locally and eventually on the cloud.
Scenario
A simple Spring Boot Getting Started web app
Before you begin
- Inside Visual Studio Code, you will need to set the salesforcedx-vscode-apex.java.home to one of the following values. MacOS: For Mac OS X 10.5 or later, run /usr/libexec/javahome in your Terminal to get the default JDK location. To find all installed JDKs, use /usr/libexec/javahome -V.
- Java Web Apps with Visual Studio Code. This tutorial shows you how to create a Java web application with Visual Studio Code. You'll learn how to run, debug, and edit the Java web app locally and eventually on the cloud. A simple Spring Boot Getting Started web app. Before you begin.
Before running and deploying this sample, you must have the Java SE Development Kit (JDK) and Apache Maven build tools on your local development environment. If you don't have, please install them.
It works with Language Support for Java by Red Hat to allow users to debug Java code within Visual Studio Code. Starting a debugging session is easy, click on the Run Debug button available at the CodeLens of your main function, or press F5. The debugger will automatically generate the proper configuration for you.
Download and install the Java Extension Pack, which has JDK 11 included.
Note: The JAVA_HOME environment variable must be set to the install location of the JDK to complete this tutorial.
Download Apache Maven version 3 or greater:
Install Apache Maven for your local development environment:
Download and test the Spring Boot app
Clone the Spring Boot Getting Started sample project to your local machine. You can clone a Git repository with the Git: Clone command in the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)). Paste https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-spring-boot.git as the URL of the remote repository and then decide the parent directory under which to put the local repository. After that, open the complete folder within the cloned repository in VS Code by navigating to the folder and typing code ..
Note: You can install Visual Studio Code from https://code.visualstudio.com and Git from https://git-scm.com.
From within VS Code, open any of the Java files within the complete folder (for example srcmainjavahelloApplication.java). If you don't have the Java language extensions installed for VS Code, you will be prompted to install the Microsoft Java Extension Pack. Follow the instructions and reload VS Code after the installation.
Once you have the Java Extension Pack installed, it will automatically build the project for you (this may take several minutes). You can run the application within VS Code by pressing F5 and selecting the Java environment. The Java Debug extension will generate a debugging configuration file launch.json for you under a .vscode folder in your project. You can see build progress in the VS Code Status Bar and when everything is finished, the final active debug configuration is displayed.
You can learn more about how VS Code launches your application in Debugging Launch Configurations. Press F5 again to launch the debugger.
Test the web app by browsing to http://localhost:8080 using a web browser. You should see the following message displayed: 'Greetings from Spring Boot!'.
Make a change
Let's now edit HelloController.java to change 'Greetings from Spring Boot!' to something else like 'Hello World'. VS Code provides a great editing experience for Java, check out Editing and Navigating Code to learn about VS Code's editing and code navigation features.
Click the Restart button on the top of the editor to relaunch the app and see result by reloading the browser.
Debug the application
Set a breakpoint (F9) in the application source code, and reload your browser to hit the breakpoint.
If you would like to learn more about debugging Java with VS Code, you can read Java Debugging.
Congratulations, you have your first Spring Boot web app running locally! Read on to learn how to host it in the cloud.
Deploy Web Apps to the cloud
We just built a Java web application and ran it locally. Now you will learn how to deploy from Visual Studio Code and run it on Azure in the cloud.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, you can sign up for a free Azure account. Create your free Azure account
Install the Azure App Service extension
The Azure App Service extension is used to create, manage, and deploy to Azure App Service with key features including:
- Create new Azure Web App/Deployment Slot
- Deploy to Azure Web App/Deployment Slot
- Start, stop, and restart the Azure Web App/Deployment Slot
- View a Web App's log files
- Swap Deployment Slots
To install the Azure App Service extension, open the Extensions view (⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)) and search for azure app service to filter the results. Select the Microsoft Azure App Service extension. For a more command-line Maven-centric experience, you can also check out the Maven plugin for Azure App Service Linux tutorial.
Create a new Web App on Azure
Once the extension is installed, you can take the following steps to create a new Web App on Azure.
- Click Create New Project button on the APP SERVICE Explorer view.
- Select a subscription.
- Enter a unique name for the new Web App.
- Select a location for the new Web App.
- Select the OS as
Linux. - Select the runtime of the Web App, for example
Tomcat 8.5 (JRE8).
Build and deploy to a Web App
The deploy process leverages the Azure Account extension (installed along with the Azure App Service extension as a dependency) and you need to sign in with your Azure subscription. If you do not have an Azure subscription, sign up today for a free 30 day account and get $200 in Azure Credits to try out any combination of Azure services.
To sign in to Azure, run Azure: Sign In from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)). You can then sign in to your account using the Device Login flow. Select Copy & Open to open your default browser.
Paste in the access code and continue the sign in process.
Once you have signed in, you can open the command prompt or terminal window and build the project using Maven commands. This will generate a new war or jar artifact in the target directory.
After building the project, open the target directory in VS Code Explorer. Right-click on the artifact and choose Deploy to Web App, and follow the prompts to choose the Web App for your deployment.
Open the Output window in VS Code to view the deployment logs. Once the deployment is completed, it will print out the URL for your Web App. Click the link to open it in a browser, you can see the web app running on Azure!
Note: For more advanced features of App Service, you can check out the Azure App Service extension.
Connect with data services
Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed database service that allows developers to work with data using a variety of standard APIs, such as SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Graph, and Table.
The Spring Boot Starter makes it easy to store data in and retrieve data from your Azure Cosmos DB with SQL API.
Create an Azure Cosmos DB entity on Azure
- Go to Azure portal and click the '+' to Create a resource.
- Click Databases, and then click Azure Cosmos DB to create your database.
- Select SQL (Document DB) API and type in other information for your database.
- Navigate to the database you have created, click Keys, and copy your URI and PRIMARY KEY for your database.
Config your project
You can start from the Spring Data Azure Cosmos DB Sample Project.
Navigate to
src/main/resourcesand openapplication.properties. Replace below properties inapplication.propertieswith information of your database.
Run and debug the application
You can press F5 to run your application. To check the result, open Azure portal and access your Cosmos DB. Click Data Explorer, and next choose Documents. You will see data being shown if it is successfully written into Cosmos DB. You can also browse your data entries in Cosmos DB with Azure Databases extension.
After setting a breakpoint (F9) in your source code, refresh your browser to hit the breakpoint. Details about debugging can be found in Java Debugging
Alternatively, you can also use Maven to package and run your project as steps below:
Navigate to the directory
azure-spring-bootand run the command.Navigate to the directory
azure-documentdb-spring-boot-sampleand run the command.
Next steps
- To containerize and deploy a web application, check out the Docker Container Tutorial.
- To learn more about Java Debugging features, see the Java Debugging Tutorial.
This tutorial shows you how to write and run Hello World program in Java with Visual Studio Code. It also covers a few advanced features, which you can explore by reading other documents in this section.
For an overview of the features available for Java in VS Code, see Java Language Overview
If you run into any issues when following this tutorial, you can contact us by clicking the Report an issue button below.
Setting up VS Code for Java development
Coding Pack for Java
To help you set up quickly, you can install the Coding Pack for Java, which includes VS Code, the Java Development Kit (JDK), and essential Java extensions. The Coding Pack can be used as a clean installation, or to update or repair an existing development environment.
Install the Coding Pack for Java - macOS
Note: The Coding Pack for Java is only available for Windows and macOS. For other operating systems, you will need to manually install a JDK, VS Code, and Java extensions.
Android Studio Jdk Download
Installing extensions
If you are an existing VS Code user, you can also add Java support by installing Java Extension Pack, which includes these extensions:
The Java Extension Pack provides a Quick Start guide and tips for code editing and debugging. It also has a FAQ that answers some frequently asked questions. Use the command Java: Getting Started from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) to launch the guide.
You can also install extensions separately. The Extension Guide is provided to help you. You can launch the guide with the Java: Extension Guide command.
For this tutorial, the only required extensions are:
Settings for the JDK
Supported Java versions
The supported version for running the VS Code for Java extension and the supported version for your projects are two separate runtimes. To run VS Code for Java, Java SE 11 or above version is required; for projects, VS Code for Java supports projects with version 1.5 or above. For more details, refer to Configure JDK.
Android Studio Jdk
Using Java runtime configuration wizard
To help you configure correctly, we provide a runtime configuration wizard. You can launch the wizard by opening the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) and typing the command Java: Configure Java Runtime, which will display the configuration user interface below.
Note: To configure multiple JDKs, see Configure JDK. To enable Java preview features, see How can I use VS Code with new Java versions
Using VS Code settings
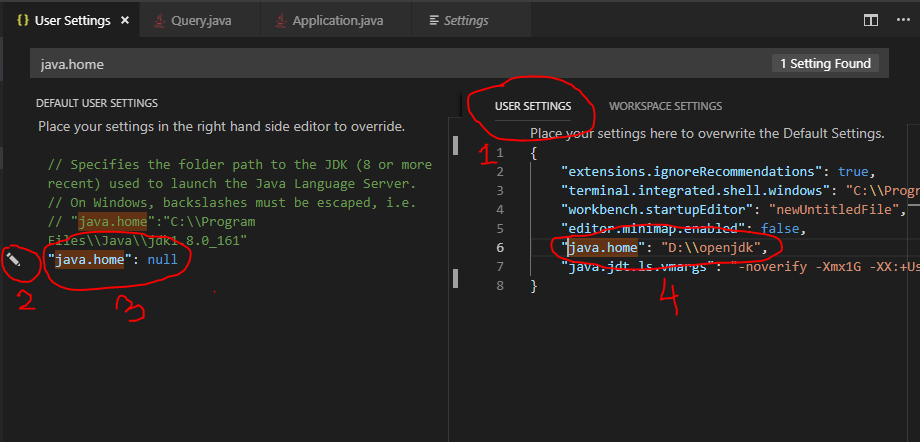
Alternatively, you can configure JDK settings using the VS Code Settings editor. A common way to do this is setting the value of the JAVA_HOME system environment variable to the install location of the JDK, for example, C:Program FilesJavajdk-13.0.2. Or if you want to configure only VS Code to use the JDK, use the java.home setting in VS Code's User or Workspace settings.
Installing a Java Development Kit (JDK)
When you need install a JDK, we recommend you to consider installing from one of these sources:
Creating a source code file
Create a folder for your Java program and open the folder with VS Code. Then in VS Code, create a new file and save it with the name Hello.java. When you open that file, the Java Language Server automatically starts loading, and you should see a loading icon on the right side of the Status Bar. After it finishes loading, you will see a thumbs-up icon.
Note: If you open a Java file in VS Code without opening its folder, the Java Language Server might not work properly.
VS Code will also try to figure out the correct package for the new type and fill the new file from a template. See Create new file.
You can also create a Java project using the Java: Create Java Project command. Bring up the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) and then type java to search for this command. After selecting the command, you will be prompted for the location and name of the project. You can also choose your build tool from this command.
Visual Studio Code also supports more complex Java projects, see Project Management.
Editing source code
You can use code snippets to scaffold your classes and methods. VS Code also provides IntelliSense for code completion, and various refactor methods.
To learn more about editing Java, see Java Editing.
Running and debugging your program
To run and debug Java code, set a breakpoint, then either press F5 on your keyboard or use the Run > Start Debugging menu item. You can also use the Run|Debug CodeLens options in the editor. After the code compiles, you can see all your variables and threads in the Run view.
The debugger also supports advanced features such as Hot Code replacement and conditional breakpoints.
For more information, see Java Debugging.
Android Studio Jdk Setting
More features
Android Studio Jdk Version
The editor also has much more capability for your Java workload.
Configure Jdk In Visual Studio Code
- Editing Java explains how to navigate and edit Java in more details
- Debugging illustrates all the key features of the Java Debugger
- Testing provides comprehensive support for JUnit and TestNG framework
- Java Project Management shows you how to use a project view and work with Maven
- Spring Boot and Tomcat and Jetty demonstrate great framework support
- Java Web Apps shows how to work with Java Web App in VS Code
